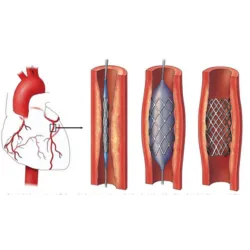
Angiography and Angioplasty
Angiography is used to examine the blood vessels and determine if there are any potential heart conditions. However, angioplasty uses narrowed arteries to treat the condition.

Angiography is used to examine the blood vessels and determine if there are any potential heart conditions. However, angioplasty uses narrowed arteries to treat the condition.